If you’re here, you’re dealing with a P0171 error code. This trouble code is one of the most common diagnostic codes that vehicle owners encounter. Whether you’ve spotted it using an OBD-II scanner or had it flagged during a vehicle inspection, understanding what the P0171 code means is crucial for resolving the issue and maintaining your vehicle’s performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain what the P0171 code is, its potential causes, symptoms, and how to fix it. By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge needed to diagnose and resolve this error efficiently.
What Is the P0171 Code?
The P0171 code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that stands for “System Too Lean (Bank 1).”
When your vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system detects that the engine is running too lean on Bank 1 (the side of the engine containing cylinder 1), it triggers this code. A “lean” condition means there is too much air and not enough fuel in the combustion process, which can affect your engine’s performance and fuel efficiency.

What Causes the P0171 Code?
There are several reasons why your engine might be running too lean. The most common causes include:
- Vacuum Leaks
- A vacuum leak allows unmetered air to enter the engine, disrupting the air-to-fuel ratio. This can occur due to cracked vacuum hoses, a faulty intake manifold gasket, or a broken PCV valve.
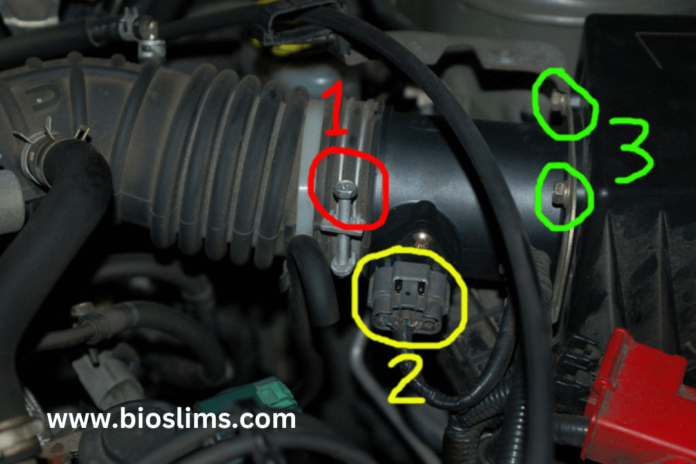
- Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF)
- The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. If it sends incorrect readings, it can cause the engine to run lean.
- Clogged or Failing Fuel Injectors
- Fuel injectors deliver fuel to the engine. If they’re clogged or malfunctioning, the engine might not receive enough fuel, leading to a lean condition.
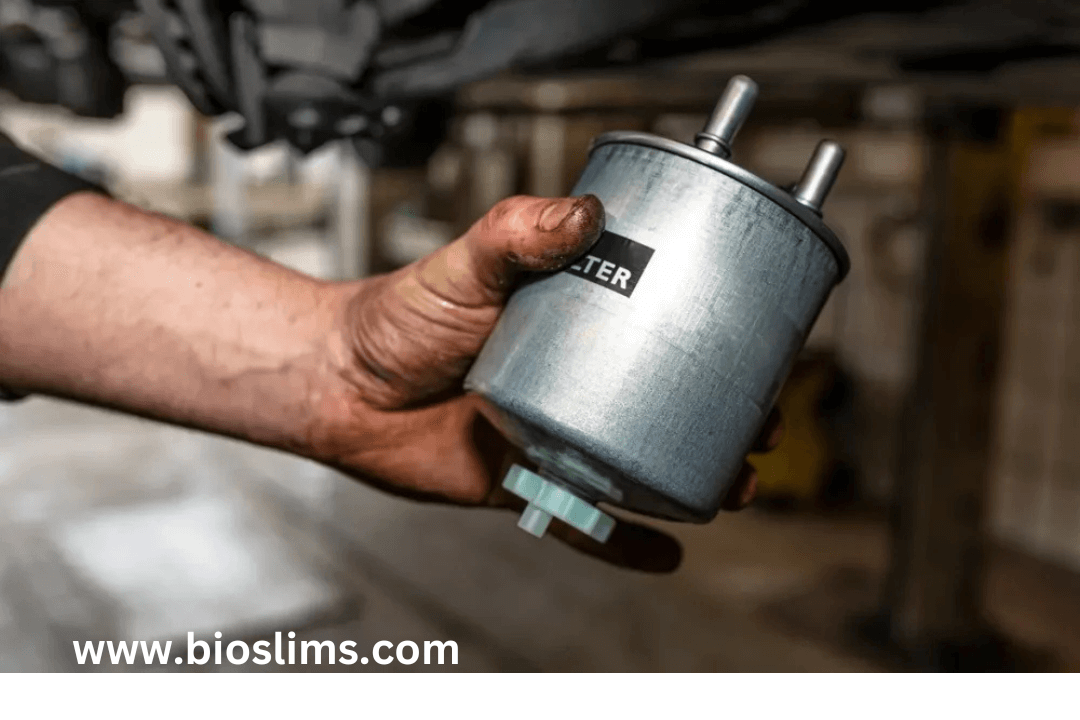
- Weak Fuel Pump or Low Fuel Pressure
- A failing fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel delivery, resulting in a lean mixture.
- Exhaust System Leaks
- Leaks in the exhaust system near the oxygen sensors can cause false readings, leading to the P0171 code.
- Malfunctioning Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors)
- Faulty oxygen sensors may send inaccurate data to the engine control module (ECM), causing an improper fuel-air mixture.
- Dirty or Failing Engine Air Filter
- A clogged air filter can restrict airflow, affecting the fuel-air ratio.
- Software Issues in the ECM
- Occasionally, the ECM software may need updating or reprogramming to address P0171 issues.
Symptoms of the P0171 Code
If your vehicle is throwing the P0171 code, you may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Check Engine Light (CEL)
- The most obvious sign is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Reduced Engine Performance
- A lean air-fuel mixture can cause hesitation, poor acceleration, or a noticeable loss of power.
- Rough Idling
- Your engine may idle erratically or stall when the P0171 code is present.
- Increased Fuel Consumption
- A lean condition can disrupt fuel efficiency, causing you to use more fuel than usual.
- Misfires
- Lean conditions can lead to engine misfires, which may result in a rough ride or noticeable vibrations.
- Unusual Exhaust Odor
- In some cases, you may detect a strange odor from the exhaust due to an improper air-fuel mixture.
How to Diagnose the P0171 Code
Proper diagnosis is essential to fix the P0171 code. Here’s a step-by-step guide to identifying the root cause:
Step 1: Use an OBD-II Scanner
- Connect an OBD-II scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port to retrieve the P0171 code and any related codes (e.g., P0174 for Bank 2).
Step 2: Inspect for Vacuum Leaks
- Check vacuum hoses, the intake manifold, and the PCV valve for cracks, disconnections, or leaks. A smoke test can help detect hard-to-find leaks.
Step 3: Examine the MAF Sensor
- Inspect the MAF sensor for dirt or damage. Clean it with a specialized MAF cleaner if needed.
Step 4: Test the Fuel System
- Check the fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel injectors for proper operation. Use a fuel pressure gauge to ensure the fuel pressure meets manufacturer specifications.
Step 5: Inspect the Oxygen Sensors
- Test the upstream oxygen sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) for proper functionality. If it is sending incorrect readings, replace it.
Step 6: Check the Air Filter
- Ensure the air filter is clean and free of obstructions. Replace it if necessary.
Step 7: Examine the Exhaust System
- Inspect for exhaust leaks near the oxygen sensors or catalytic converter.
Step 8: Update the ECM Software
- Consult a dealership or qualified mechanic to check for ECM software updates that may address the issue.
How to Fix the P0171 Code
Once you’ve diagnosed the problem, here are the most common fixes for the P0171 code:
- Repair Vacuum Leaks
- Replace damaged or disconnected vacuum hoses, intake manifold gaskets, or the PCV valve.
- Clean or Replace the MAF Sensor
- Clean the MAF sensor using a dedicated cleaner. If cleaning doesn’t work, replace the sensor.
- Replace Fuel Injectors or Fuel Filter
- Clean clogged fuel injectors or replace them if they’re faulty. Also, replace the fuel filter if it’s restricting fuel flow.
- Fix Exhaust System Leaks
- Seal any leaks in the exhaust system, especially near the oxygen sensors.
- Replace Faulty Oxygen Sensors
- Install new upstream oxygen sensors if they’re sending incorrect data to the ECM.
- Replace the Air Filter
- Install a clean air filter to ensure proper airflow to the engine.
- Update or Reprogram the ECM
- If all else fails, consult a professional mechanic to update or reprogram the ECM.
Preventing the P0171 Code
Preventative maintenance can help you avoid the P0171 code and similar issues. Here are some tips:
- Regularly Inspect and Replace Components
- Check your air filter, fuel filter, and spark plugs periodically and replace them as needed to maintain optimal engine performance.
- Clean the MAF Sensor
- Clean the MAF sensor at least once a year to prevent dirt buildup.
- Use High-Quality Fuel
- Using high-quality fuel can prevent clogging and buildup in the fuel system.
- Monitor Vacuum Hoses and Seals
- Regularly inspect vacuum hoses and intake seals for cracks or leaks.
- Perform Routine Maintenance
- Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule to keep your engine running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can I Drive With a P0171 Code?
While it’s possible to drive with a P0171 code, it’s not advisable. A lean condition can cause long-term damage to your engine and catalytic converter if left unaddressed.
- How Much Does It Cost to Fix the P0171 Code?
The cost of fixing the P0171 code depends on the root cause. For example:
- Replacing a vacuum hose: $50-$150
- Cleaning the MAF sensor: $10-$50 (if you do it yourself)
- Replacing an oxygen sensor: $150-$500
- Repairing fuel system components: $200-$1,000+
- Can a Dirty Air Filter Cause a P0171 Code?
Yes, a dirty or clogged air filter can restrict airflow and contribute to a lean condition, triggering the P0171 code.
- How Long Does It Take to Fix a P0171 Code?
The repair time depends on the issue. Simple fixes like replacing a vacuum hose or
You may also read: How Many Pints in a Gallon? Everything You Need to Know